Alvar Woodland
- System
- Terrestrial
- Subsystem
- Barrens And Woodlands
- State Protection
- Not Listed
Not listed or protected by New York State.
- Federal Protection
- Not Listed
- State Conservation Status Rank
- S2
Imperiled in New York - Very vulnerable to disappearing from New York due to rarity or other factors; typically 6 to 20 populations or locations in New York, very few individuals, very restricted range, few remaining acres (or miles of stream), and/or steep declines.
- Global Conservation Status Rank
- G2?
Imperiled globally (most likely) - Conservation status is uncertain, but most likely at high risk of extinction due to rarity or other factors; typically 20 or fewer populations or locations in the world, very few individuals, very restricted range, few remaining acres (or miles of stream), and/or steep declines. More information is needed to assign a firm conservation status.
Summary
Did you know?
Alvar is a Swedish term to describe barrens and grassland vegetation growing on thin soils over level outcrops of limestone or dolomite bedrock. This community is limited to areas in Jefferson County underlain with Chaumont limestone (Galoo-Rock outcrop complex).
State Ranking Justification
There are probably much less than 30 occurrences statewide. A few documented occurrences have good viability and several are protected on public land or private conservation land. This community is limited to areas in Jefferson County underlain with Chaumont limestone (Galoo-Rock outcrop complex), and there are only a few high quality examples. The current trend of this community is probably stable for occurrences on public land and private conservation land, or declining slightly elsewhere due to moderate threats that include conversion to pastureland, development, trampling by visitors, ATVs, and invasive species.
Short-term Trends
It is estimated that alvar woodland acreage has declined 10-30% within the last 100 years.
Long-term Trends
The current acreage is estimated to be less than half of the historical acreage.
Conservation and Management
Threats
Threats are the invasion of exotic plants (in particular pale swallow-wort, buckthorn, and honeysuckles), grazing, trampling (especially ORV damage), hydrologic alterations, and development pressure in Jefferson County.
Conservation Strategies and Management Practices
Maintain the mosaic proportional distribution of existing alvar communities by ensuring the the pavement areas and grasslands are kept open. Alvar communities seem to require seasonal flooding, and maintenance of the natural hydrologic regime is critical. Take measures to exclude use of sites by ORVs. Prescribed fire may be a useful tool to promote native plant species diversity (care should be taken in selecting sites for its introduction) and the maintanence of open site conditions (Kost et al. 2007). Develop and implement a prescribed burn plan at appropriate sites. Improve the condition of existing alvar communities by reducing and/or eliminating invasive species, such as black swallow-wort (Cynanchum louiseae), Morrow's honeysuckle (Lonicera morrowii), and buckthorn (Rhamnus cathartica). Identify and target areas with early infestations of invasive exotic plants for control and eradication. Improve the condition of the alvar communities by minimizing trail network and clearly marking existing trails. Improve the landscape context of the barrens by encouraging surrounding landowners to establish natural buffers and restore natural corridors to other larger natural landscape blocks.
Development and Mitigation Considerations
Soils are very thin or lacking in and around this community and the effect of clearing and construction on soil retention and erosion must be considered during any development activities. Similarly, these pavements have wide cracks and fissures and any soil enrichment contamination (e.g., from septic leach fields and fertilized lawns) may rapidly alter the water quality of underlying aquifers as well as altering the barrens community structure and function.
Inventory Needs
The alvar communities in Jefferson County need to be inventoried and remapped using the current classification of alvar communities: 1) alvar pavement grassland, 2) alvar shrubland, 3) alvar woodland, 4) dry alvar grassland, and 5) wet alvar grassland. Survey for additional occurrences in Jefferson County and the surrounding region to advance documentation and classification of alvar woodlands. Continue searching for large sites in excellent to good condition (A- to AB-ranked). Periodic inventory of the alvar woodlands is needed, in order to keep occurrence data current. Quantitative data on composition and variability among patches within occurrences are needed from surveys throughout the growing season. Surveys for rare and characteristic invertebrate species (especially butterflies and moths, along with terrestrial molluscs) are needed for many sites.
Research Needs
Research the composition of alvar woodlands in Jefferson County in order to characterize variations and distinguish it from other alvar communities. Studies of the hydrology of alvar communities (a past study was conducted at Chaumont Barrens) and their immediately surrounding landscape are needed to better understand their hydrologic regimes. Continue long-term monitoring of deer browsing and grazing impacts. Establish a monitoring progam at various sites to understand and track the development of impacts from global climate change. Identify areas where fire can be implemented and evaluated as a management tool, including a flora and fauna monitoring component (Reschke et al. 1999).
Rare Species
- Carex backii (Back's Sedge) (guide)
- Carex molesta (Troublesome Sedge) (guide)
- Carex richardsonii (Richardson's Sedge) (guide)
- Castilleja coccinea (Indian Paintbrush) (guide)
- Cirriphyllum piliferum (Hair-pointed Moss) (guide)
- Corydalis aurea (Golden Corydalis) (guide)
- Cypripedium arietinum (Ram's Head Lady's Slipper) (guide)
- Didymodon ferrugineus (Rusty Beard-moss) (guide)
- Epilobium hornemannii ssp. hornemannii (Alpine Willowherb) (guide)
- Gentianopsis virgata (Lesser Fringed Gentian) (guide)
- Geum virginianum (Cream-colored Avens) (guide)
- Myurella julacea (Small Mousetail Moss) (guide)
- Platydictya jungermannioides (False Willow Moss) (guide)
- Ulmus thomasii (Rock Elm) (guide)
Range
New York State Distribution
Restricted to outcrops of Chaumont limestone (Galoo-Rock outcrop complex) in Jefferson County. New York's sites are at the easternmost edge of a narrow range extending across southern Ontario to the eastern edge of northern Michigan. There are about 54 square miles (34,368 acres) of Galoo-Rock outcrop complex mapped in Jefferson County in the Soil Survey Geographic (SSURGO) database for New York.
Global Distribution
This alvar woodland type is scattered throughout the Great Lakes region of the United States and Canada, from southern Ontario and northern Michigan to northern New York (NatureServe Explorer 2015).
Best Places to See
- Limerick Cedars Preserve (Jefferson County)
- Ashland Flats WMA (Jefferson County)
- Chaumont Barrens Preserve (Jefferson County)
Identification Comments
General Description
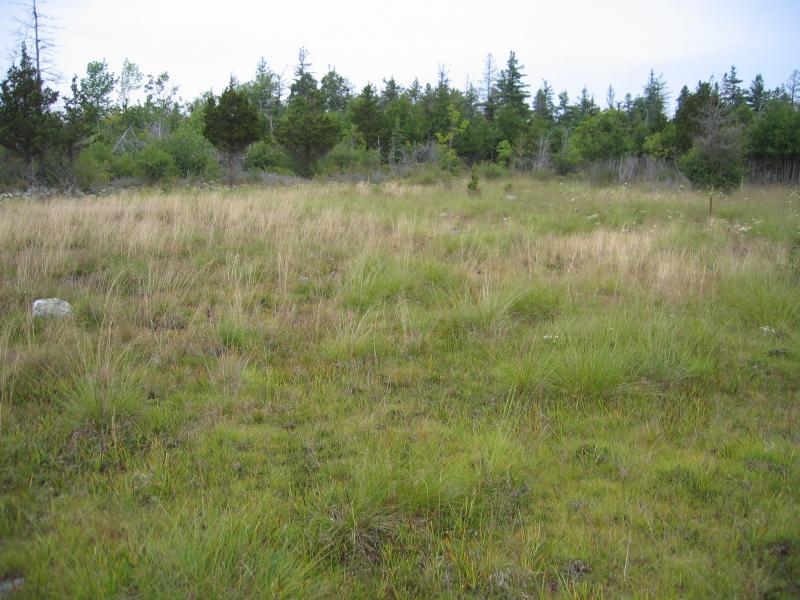
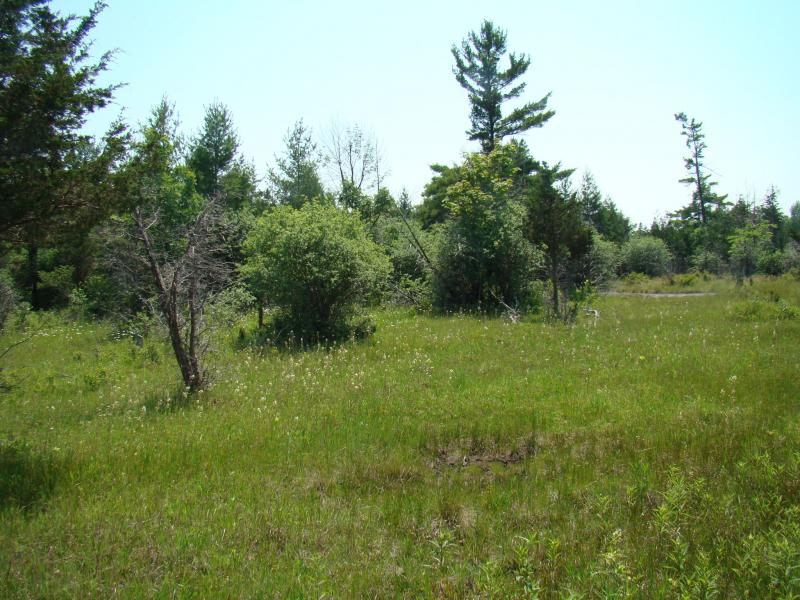
The woodland tree canopy consists of a variable mixture of eastern red cedar (Juniperus virginiana), northern white cedar (Thuja occidentalis), bur oak (Quercus macrocarpa), white ash (Fraxinus americana), paper birch (Betula papyrifera), white pine (Pinus strobus), shagbark hickory (Carya ovata), hop hornbeam (Ostrya virginiana), white spruce (Picea glauca), balsam fir (Abies balsamea), basswood (Tilia americana), American elm (Ulmus americana), rock elm (U. thomasii), and pin-cherry (Prunus pensylvanica). The understory of this is a mosaic of shrubby patches, exposed pavement, and grassy patches. The most abundant shrub is common juniper (Juniperus communis); other characteristic shrubs include buffaloberry (Shepherdia canadensis) and bearberry (Arctostaphylos uva-ursi). Characteristic herbs include false pennyroyal (Trichostema brachiatum), Crawe's sedge (Carex crawei), balsam ragwort (Packera paupercula), ebony sedge (Carex eburnea), and sheathed rush grass (Sporobolus vaginiflorus). Areas of exposed limestone or dolostone pavement are common, usually with a cover of mosses such as Tortella spp. and Schistidium spp., lichens such as reindeer lichen (Cladonia rangiferina) and dog-lichen (Peltigera canina), and rock surface algae (Gloeocapsa alpina).
Characters Most Useful for Identification
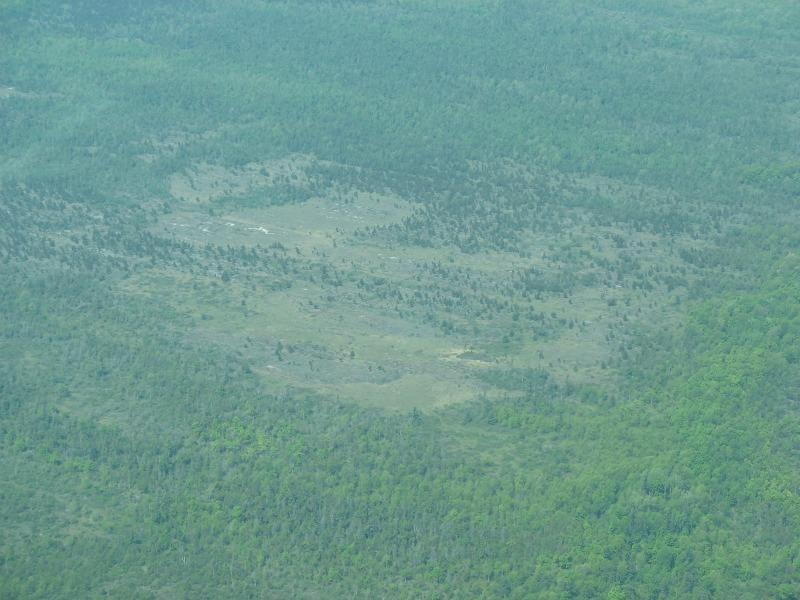
This community is a mixed conifer woodland that occurs on shallow soils over limestone bedrock in alvar settings, and usually includes numerous rock outcrops. Alvar woodlands occur on Chaumont limestone (Galoo-Rock outcrop complex) within a mosaic of other alvar communities.
Elevation Range
Known examples of this community have been found at elevations between 258 feet and 410 feet.
Best Time to See
These mixed conifer woodlands can be seen throughout the year. The coniferous treees are easier to spot during the winter months while the woodland wildflowers are best seen during April and May.
Alvar Woodland Images
Classification
International Vegetation Classification Associations
This New York natural community encompasses all or part of the concept of the following International Vegetation Classification (IVC) natural community associations. These are often described at finer resolution than New York's natural communities. The IVC is developed and maintained by NatureServe.
- Eastern Red-cedar / Early Buttercup Woodland (CEGL005122)
- Jack Pine - Northern White-cedar - White Spruce / Common Juniper Woodland (CEGL005126)
NatureServe Ecological Systems
This New York natural community falls into the following ecological system(s). Ecological systems are often described at a coarser resolution than New York's natural communities and tend to represent clusters of associations found in similar environments. The ecological systems project is developed and maintained by NatureServe.
- Great Lakes Alvar (CES201.721)
Characteristic Species
-
Trees > 5m
- Abies balsamea (balsam fir)
- Betula papyrifera (paper birch)
- Carya ovata var. ovata (shagbark hickory)
- Fraxinus americana (white ash)
- Juniperus virginiana var. virginiana (eastern red cedar)
- Ostrya virginiana (hop hornbeam, ironwood)
- Picea glauca (white spruce)
- Pinus banksiana (jack pine)
- Pinus strobus (white pine)
- Prunus pensylvanica (pin cherry, fire cherry)
- Quercus macrocarpa (bur oak)
- Thuja occidentalis (northern white cedar, arbor vitae)
- Tilia americana var. americana (American basswood)
- Ulmus americana (American elm)
- Ulmus thomasii (rock elm)
-
Shrubs < 2m
- Arctostaphylos uva-ursi (bearberry)
- Juniperus communis var. depressa (American common juniper, ground juniper)
- Shepherdia canadensis (Canada buffalo-berry)
-
Herbs
- Carex crawei (Crawe's sedge)
- Carex eburnea (bristle-leaved sedge)
- Packera paupercula (balsam groundsel)
- Sporobolus vaginiflorus var. vaginiflorus (poverty dropseed)
- Trichostema brachiatum (false pennyroyal)
-
Nonvascular plants
- Cladonia rangiferina
- Gloeocapsa alpina
- Peltigera canina
- Schistidium spp.
- Tortella spp.
Similar Ecological Communities
- Alvar shrubland
(guide)
Alvar shrublands have less than 25% cover of trees and have over 25% cover of dwarf, short, and tall shrubs (avg. 43% cover of shrubs). Alvar woodlands have over 25% cover of trees 5 m or taller.
- Calcareous pavement woodland
(guide)
Calcareous pavement woodlands occur statewide in areas underlain by various limestone bedrock types in a non-alvar landscape. Alvar woodlands occur on Chaumont limestone (Galoo-Rock outcrop complex) within a mosaic of other alvar communities.
- Dry alvar grassland
(guide)
Dry alvar grasslands typically lack trees and are dominated by poverty grass (Danthonia spicata). Alvar woodlands have over 25% cover of trees 5 m or taller.
- Limestone woodland
(guide)
Limestone woodlands occur statewide in areas underlain by various limestone bedrock types in a non-alvar landscape. Alvar woodlands occur on Chaumont limestone (Galoo-Rock outcrop complex) within a mosaic of other alvar communities.
- Wet alvar grassland
(guide)
Wet alvar grasslands typically lack trees and are dominated by tufted hairgrass (Deschampsia cespitosa), Crawe's sedge (Carex crawei), prairie dropseed (Sporobolus heterolepis), and flat-stemmed spikerush (Eleocharis elliptica var. elliptica). Alvar woodlands have over 25% cover of trees 5 m or taller.
Vegetation
Percent cover
This figure helps visualize the structure and "look" or "feel" of a typical Alvar Woodland. Each bar represents the amount of "coverage" for all the species growing at that height. Because layers overlap (shrubs may grow under trees, for example), the shaded regions can add up to more than 100%.
Additional Resources
References
Edinger, G. J., D. J. Evans, S. Gebauer, T. G. Howard, D. M. Hunt, and A. M. Olivero (editors). 2014. Ecological Communities of New York State. Second Edition. A revised and expanded edition of Carol Reschke’s Ecological Communities of New York State. New York Natural Heritage Program, New York State Department of Environmental Conservation, Albany, NY. https://www.nynhp.org/ecological-communities/
Edinger, Gregory J., D.J. Evans, Shane Gebauer, Timothy G. Howard, David M. Hunt, and Adele M. Olivero (editors). 2002. Ecological Communities of New York State. Second Edition. A revised and expanded edition of Carol Reschke's Ecological Communities of New York State. (Draft for review). New York Natural Heritage Program, New York State Department of Environmental Conservation. Albany, NY. 136 pp.
Gilman, B. 1998. Alvars of New York: a site summary. Finger Lakes Community College. Canadaigua, NY.
NatureServe. 2015. NatureServe Explorer: An online encyclopedia of life [web application]. Version 7.1. NatureServe, Arlington, Virginia. Available http://www.natureserve.org/explorer.
New York Natural Heritage Program. 2024. New York Natural Heritage Program Databases. Albany, NY.
Reschke, C., R. Reid, J. Jones, T. Feeney, and H. Potter. 1999. Conserving Great Lakes Alvars: final technical report of the International Alvar Conservation Initiative. The Nature Conservancy, Great Lakes Program, Chicago, IL.
Reschke, Carol. 1990. Ecological communities of New York State. New York Natural Heritage Program, New York State Department of Environmental Conservation. Latham, NY. 96 pp. plus xi.
Links
- Conserving Great Lakes Alvars: final technical report of the International Alvar Conservation Initiative (Reschke et al. 1999).
- EPA Great Lakes Ecological Protection and Restoration Conserving Great Lakes Alvars
- NYS DEC Habitat Management Plan for Ashland Flats Wildlife Management Area
- The Nature Conservancy, New York, Chaumont Barrens Preserve
About This Guide
This guide was authored by: Gregory J. Edinger
Information for this guide was last updated on: January 23, 2024
Please cite this page as:
New York Natural Heritage Program. 2024.
Online Conservation Guide for
Alvar woodland.
Available from: https://guides.nynhp.org/alvar-woodland/.
Accessed July 26, 2024.